Now Reading: How to Improve Website Load Speed Using Content Delivery Networks
-
01
How to Improve Website Load Speed Using Content Delivery Networks
How to Improve Website Load Speed Using Content Delivery Networks

A Content Delivery Network improves website load speed by caching and distributing your website content across multiple global servers, reducing latency, lowering server load, and delivering data from the nearest location to users for faster page rendering and better performance.
Website speed has become one of the most critical factors influencing user experience, search engine rankings, and conversion rates. Slow loading pages frustrate visitors, increase bounce rates, and negatively affect brand credibility. One of the most effective and reliable ways to enhance website speed is by using a Content Delivery Network, commonly referred to as a CDN.
This evergreen guide explains how CDNs work, why they are essential for modern websites, how to choose the right provider, and how to implement and optimize a CDN for maximum performance. The goal is to provide clear, actionable, and trustworthy information that aligns with best practices and expert recommendations.
Understanding What a Content Delivery Network Is
A Content Delivery Network is a network of geographically distributed servers designed to deliver web content efficiently. Instead of serving every visitor from a single central server, a CDN stores cached copies of your website files on multiple edge servers around the world.
When a user visits your website, the CDN automatically delivers content from the nearest server location. This reduces the physical distance that data must travel, which directly lowers latency and speeds up page load times.
CDNs primarily handle static assets such as images, style sheets, JavaScript files, fonts, and sometimes video content. Many modern CDNs also support dynamic content acceleration and real time processing.
In simple terms, a CDN acts as a high performance middle layer between your website server and your visitors, ensuring fast, reliable, and secure delivery of content.
Why Website Load Speed Matters More Than Ever
Website speed affects nearly every aspect of online success. Faster websites lead to better user satisfaction, stronger search visibility, and higher engagement.
Search engines consider page speed as a ranking factor. Faster sites are more likely to appear higher in search results. Users also expect pages to load quickly. Even a delay of one second can significantly reduce conversions.
From an operational perspective, slow websites consume more server resources, increasing hosting costs and causing performance bottlenecks during traffic spikes.
Using a CDN addresses all these challenges by optimizing content delivery at scale.
Related search: Top 6 Hosting Providers with Fast Website Loading Speeds
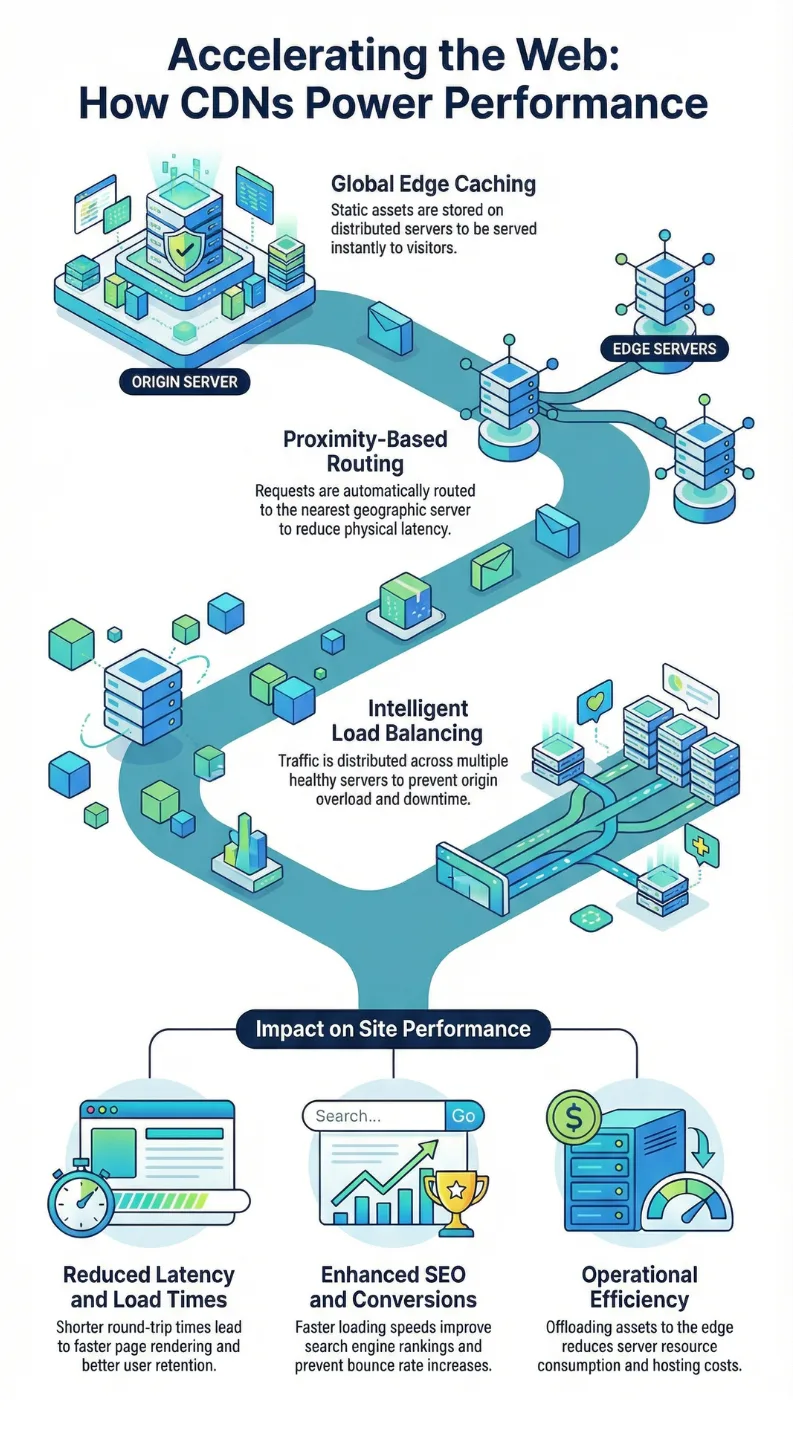
How CDNs Reduce Latency Through Geographic Distribution
Latency is the time it takes for data to travel from a server to a user’s device. The farther the distance, the higher the latency.
Without a CDN, all users must connect to your origin server, regardless of where they are located. A visitor in North America accessing a server in Asia will experience noticeable delays.
With a CDN, content is cached on servers located across multiple continents and regions. When users request your website, the CDN routes the request to the closest available server.
This geographic distribution dramatically reduces round trip time and accelerates content delivery. Pages load faster because data travels a much shorter distance.
Over time, this consistent performance improvement enhances user trust and retention.
How Content Delivery Systems Power Performance Infographic Guide
Caching as the Foundation of CDN Performance
Caching is one of the most important features of a CDN. It involves storing copies of static website assets on edge servers so they can be delivered instantly without contacting the origin server.
When a visitor requests an image, style sheet, or script, the CDN checks if a cached version is available. If it is, the CDN serves the file immediately.
This process reduces server load, minimizes bandwidth usage, and speeds up response times.
Proper caching policies ensure that assets remain fresh while still benefiting from long cache durations. This balance allows your site to deliver updated content without sacrificing performance.
Load Balancing and Traffic Distribution
Load balancing is another powerful capability provided by CDNs. It distributes incoming traffic across multiple servers rather than concentrating requests on a single origin server.
This prevents overload during high traffic periods and ensures consistent performance.
When one server becomes busy or unavailable, traffic is automatically routed to another healthy server. This redundancy improves reliability and uptime.
Load balancing also contributes to faster response times because requests are handled by servers that are operating efficiently.
For websites that experience sudden spikes in traffic, such as during product launches or promotional campaigns, load balancing is essential.
Edge Computing and Real Time Processing
Some advanced CDNs support edge computing, which allows serverless functions to run directly on edge servers.
This means certain processing tasks can be handled closer to users rather than at the origin server. Examples include personalization, authentication, and content modification.
By executing logic at the edge, websites can deliver dynamic experiences with minimal latency.
Edge computing also reduces the workload on the origin server, further improving overall performance.
Choosing the Right CDN Provider
Selecting the right CDN provider is crucial for achieving optimal results. Different providers offer varying features, pricing models, and performance capabilities.
Some well known CDN providers include Cloudflare, Akamai, Fastly, Amazon CloudFront, Google Cloud CDN, and Microsoft Azure CDN.
| Evaluation Factor | Focus |
|---|---|
| Traffic volume and expected growth | Assess whether the CDN can handle your current traffic levels and scale smoothly as your website grows. |
| Geographic distribution of your audience | Choose a provider with strong server coverage in the regions where most of your visitors are located. |
| Budget and pricing structure | Compare pricing models to ensure the CDN fits within your financial plan while offering necessary features. |
| Security features | Look for built in protections such as DDoS mitigation, firewall options, and SSL support. |
| Ease of integration | Select a CDN that offers simple setup and clear configuration options for your platform. |
| Support and documentation | Ensure the provider offers reliable technical support and detailed documentation for troubleshooting and optimization. |
Cloudflare is often favored by small to medium sized websites due to its free plan and strong security features. Akamai is widely used by large enterprises with high traffic demands. Fastly is known for real time updates and dynamic content performance.
Choose a provider that aligns with your current needs and future goals.
How to Implement a CDN Correctly
Proper implementation is essential to fully benefit from a CDN. While exact steps vary by provider, the general process includes:
- Creating an account with your chosen CDN
- Adding your website to the CDN dashboard
- Updating DNS settings to route traffic through the CDN
- Configuring your origin server
Once configured, your CDN will begin caching and serving content automatically.
Testing is important after implementation. Verify that assets are being served from CDN servers and that your site functions correctly.
Optimizing Cache Control and Headers
Cache control headers tell browsers and CDNs how long content should be stored.
Setting appropriate headers ensures that static assets are cached for long periods, while dynamic content is refreshed as needed.
Common best practices include:
- Using long cache durations for images, style sheets, and scripts
- Versioning assets to force updates when changes occur
- Avoiding unnecessary cache purges
Proper header configuration maximizes CDN efficiency and prevents stale content issues.
Compressing and Minimizing Files
CDNs work best when combined with file optimization techniques. Minification removes unnecessary characters from code without affecting functionality. Compression reduces file size before transmission.
Most CDNs support compression methods such as Gzip or Brotli. Smaller files load faster and consume less bandwidth. This leads to quicker page rendering and improved user experience.
Enabling Modern Protocols
Modern protocols such as HTTP2 and HTTP3 improve data transfer efficiency. These protocols allow multiple requests to be handled simultaneously over a single connection, reducing overhead.
Many CDNs automatically support these protocols. Enabling them ensures your site takes advantage of the latest performance enhancements.
Security Benefits That Indirectly Improve Speed
Security and performance are closely related. CDNs provide built in protection against distributed denial of service attacks, malicious bots, and other threats.
By blocking harmful traffic before it reaches your server, CDNs preserve resources for legitimate users. Some CDNs also include web application firewalls and SSL management. A secure website experiences fewer disruptions, which contributes to consistent speed and reliability.
Reducing Bandwidth Costs
Because CDNs serve cached content from edge servers, fewer requests reach your origin server. This reduces bandwidth usage and hosting expenses. Lower costs allow businesses to invest more in other performance improvements or infrastructure upgrades.
Improving SEO Through Faster Load Times
Search engines prioritize fast websites. Improved load speed leads to better crawl efficiency, higher rankings, and increased organic traffic. Faster pages also reduce bounce rates and increase dwell time, which are positive user engagement signals. By using a CDN, you indirectly strengthen your SEO performance.
Enhancing User Experience Across Devices
Users access websites from desktops, laptops, tablets, and mobile devices. A CDN ensures consistent performance across all devices and network conditions. Mobile users, who often rely on slower connections, benefit greatly from optimized content delivery. A smooth experience increases trust and encourages repeat visits.
Measuring CDN Performance
After implementing a CDN, monitor performance using tools such as:
- Page speed testing tools
- Server response time metrics
- Cache hit ratio reports
- User experience analytics
Regular monitoring helps identify optimization opportunities and ensures your CDN configuration remains effective.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even with a CDN, mistakes can limit performance gains.
Avoid these common issues:
- Not setting proper cache headers
- Caching dynamic content incorrectly
- Failing to test after changes
- Using a provider with limited global coverage
Addressing these issues ensures your CDN delivers maximum value.
When a CDN Is Most Beneficial
A CDN is beneficial for nearly all websites, but especially for:
- Sites with global audiences
- Ecommerce platforms
- Media heavy websites
- High traffic blogs
- Software as a service applications
If your site serves users in multiple regions or relies heavily on images and scripts, a CDN is essential.
Long Term Value of Using a CDN
A CDN is not a temporary solution. It is a long term investment in performance, security, and scalability. As your website grows, your CDN scales with you. This future proofing ensures consistent user experience even as traffic increases.
Best Practices for Ongoing Optimization
To maintain optimal performance:
- Regularly review cache settings
- Update assets responsibly
- Monitor analytics
- Stay informed about CDN features
- Test speed after major changes
Continuous optimization keeps your website competitive.
Conclusion
Using a Content Delivery Network is one of the most effective ways to improve website load speed, enhance user experience, and strengthen SEO. By distributing content globally, leveraging caching and load balancing, and selecting the right provider, you create a faster, more reliable, and more secure website. When implemented correctly and optimized continuously, a CDN becomes a foundational component of modern web performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a CDN in simple terms?
A CDN is a network of servers around the world that store and deliver your website content quickly to users.
Does a CDN work for small websites?
Yes, even small websites benefit from faster load times and improved reliability.
Will a CDN replace my web host?
No, a CDN works alongside your hosting provider, not as a replacement.
How long does it take to set up a CDN?
Most CDNs can be set up within minutes to a few hours.
Does a CDN help with SEO?
Yes, faster load times and better user experience improve search rankings.
Is a free CDN enough?
Free plans are suitable for many websites, but premium plans offer advanced features.
Can a CDN speed up dynamic content?
Some CDNs support dynamic acceleration and edge computing.
Do I need technical skills to use a CDN?
Basic configuration is simple, but advanced optimization may require technical knowledge.
How do I know if my CDN is working?
Use speed testing tools and check whether assets load from CDN domains.
Is a CDN secure?
Most CDNs include security features such as DDoS protection and SSL support.
Dony Garvasis is the founder of Search Ethics, a platform dedicated to transparency, authenticity, and ethical digital practices. With over 8 years of experience in SEO and digital marketing, I provide expert content on Tech, digital marketing, SEO, Artificial intelligence, gadgets, science, automobiles, lifestyle, tips, tutorials and much more. My mission is simple: Ethical Search, Genuine Results! I will make sure people everywhere get trustworthy and helpful information.










