Now Reading: How Does Vibe Coding Differ from Traditional Coding Methods
-
01
How Does Vibe Coding Differ from Traditional Coding Methods
How Does Vibe Coding Differ from Traditional Coding Methods

Vibe coding in software development is a modern approach where developers use artificial intelligence tools to generate executable code from plain English instructions instead of writing it manually. It focuses on creativity, speed, and high level goals, allowing ideas to become working software quickly while AI handles most technical implementation details.
Software development has traditionally required deep technical expertise, mastery of programming languages, and careful attention to syntax and structure. Vibe coding introduces a different mindset. Rather than concentrating on how to write code, developers focus on what they want the software to do. This shift has significant implications for productivity, accessibility, and the future role of developers.
What is vibe coding in software development
Vibe coding is an emerging and loosely defined practice where artificial intelligence systems generate software code based on natural language prompts provided by a user. Instead of manually writing functions, classes, and logic step by step, a developer describes the desired outcome in everyday language. The AI then translates that description into working code.
The term was introduced by renowned computer scientist Andrej Karpathy in early 2025 and quickly gained attention within the software community. The phrase reflects the idea of fully giving in to the creative flow or vibe of building software, trusting AI to handle the mechanical details.
In vibe coding, tools such as ChatGPT, OpenAI Codex, and Claude act as the primary code generators. Developers interact with these tools conversationally, refining prompts and giving feedback until the output behaves as expected. The emphasis is not on perfect code structure but on quickly achieving functional results.
The core philosophy behind vibe coding
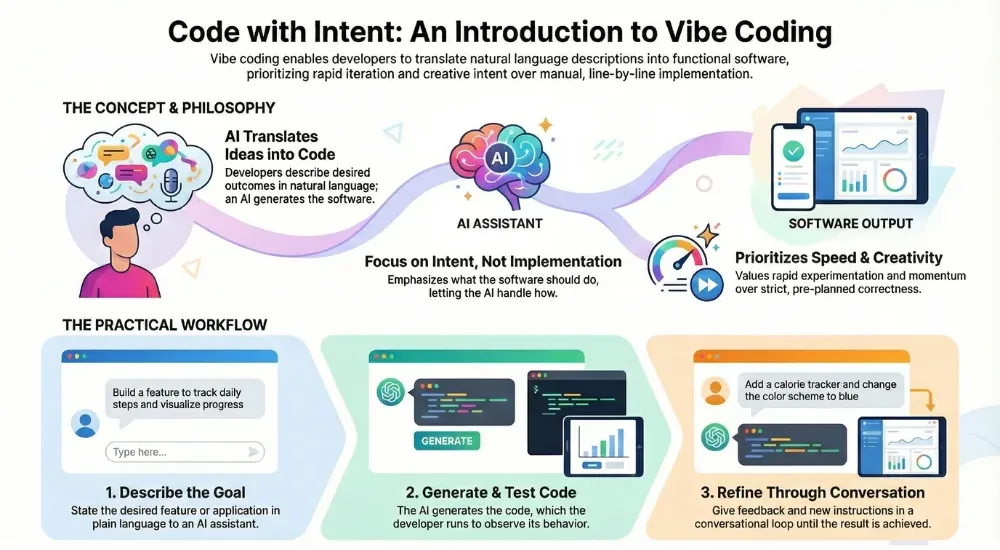
At its core, vibe coding encourages developers to focus on intent rather than implementation. Traditional development demands precision at every stage, while vibe coding accepts a degree of abstraction and uncertainty. The philosophy is to prioritize experimentation, learning, and rapid iteration.
This approach values momentum and creativity over strict correctness. Developers often do not review every line of generated code. Instead, they test the output, observe behavior, and adjust prompts accordingly. This creates a loop where ideas are quickly translated into software and refined through interaction rather than detailed planning.
Vibe coding also reflects a broader cultural shift in technology, where tools are becoming more intuitive and conversational. Just as design tools and content creation platforms have become more accessible, software development is now opening up to a wider audience.
Introduction to Vibe Coding Concept Infographic
How vibe coding works in practice
The practical workflow of vibe coding is simple but powerful. A developer begins by selecting an AI coding assistant platform. They then describe their desired application or feature in natural language. This description might include functionality, user interactions, or constraints.
The AI generates code based on this prompt. The developer runs the code, tests it, and provides feedback or additional instructions. This conversational loop continues until the result meets expectations.
For example, a user might say they want a simple expense tracking application that records daily spending and shows monthly totals. The AI generates the necessary logic, user interface elements, and data handling code. The user can then request changes such as adding categories or exporting reports, all without writing code manually.
Key characteristics of vibe coding
Vibe coding can be understood through several defining characteristics that distinguish it from other development methods.
| Characteristic Name | Description | Primary Benefit | Development Focus | Impact on Workflow |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Language Interaction | Plain English is used as the primary interface for programming. | Accessibility and ease of communication with the development environment. | Communicating ideas and instructions via language. | Shift from syntax heavy coding to descriptive prompts. |
| AI Driven Implementation | AI systems handle the responsibility for low level implementation details. | Human developers can focus on high level goals and outcomes. | System architecture and desired final results. | Delegation of routine coding tasks to automated systems. |
| Speed and Iteration | The ability to move from an initial idea to a prototype in minutes. | Rapid prototyping and quick turnaround times. | Project velocity and iterative cycles. | Shortens the timeline between conceptualization and realization. |
| Experimental Freedom | A development environment where the cost of failure is significantly lowered. | Increased willingness to innovate and try new ideas. | Experimentation and continuous learning. | Encourages a trial and error approach without heavy penalties. |
| Reduced Scrutiny | Lower levels of code scrutiny are often accepted for specific project types. | Faster development and less overhead for non production code. | Functionality over strict code perfection. | Streamlines development by bypassing some traditional review rigor. |
Vibe coding versus traditional coding methods
Vibe coding differs from traditional coding methods in several fundamental ways, affecting philosophy, workflow, and outcomes.
Development approach and mindset
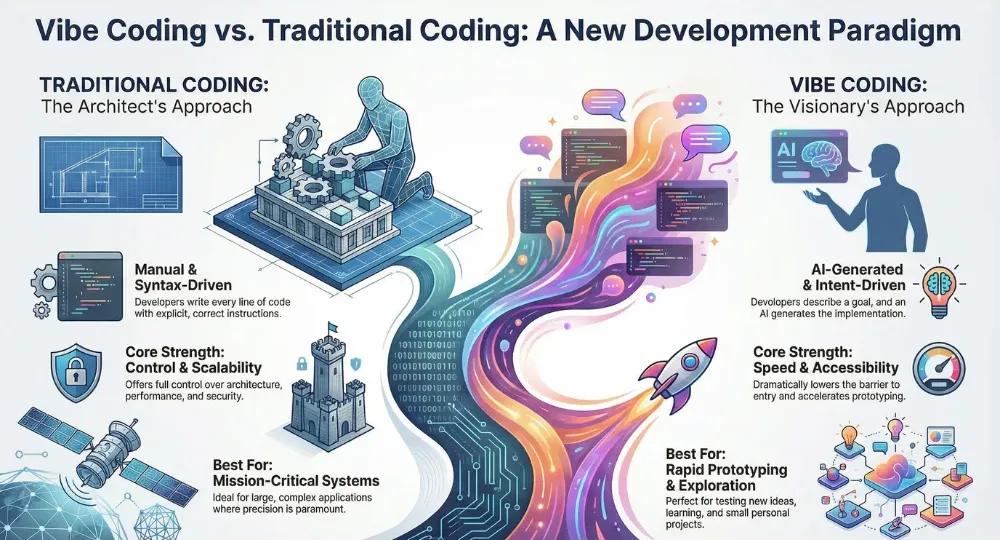
Traditional coding requires developers to manually write code using programming languages such as Python, Java, or C++. Every instruction must be explicit and correct. This approach emphasizes control, structure, and deep technical understanding.
Vibe coding replaces much of this manual effort with AI generated code. Developers describe what they want, and the AI determines how to implement it. The focus shifts from syntax mastery to problem definition and creative thinking.
Accessibility and learning curve
Traditional coding has a steep learning curve. Beginners must learn syntax, data structures, algorithms, and debugging techniques before building useful applications.
Vibe coding dramatically lowers this barrier. People with little or no programming experience can create functional software by describing their needs. This democratizes software development and allows more people to participate in building digital tools.
Speed and efficiency
Manual coding can be time consuming, especially for repetitive tasks or boilerplate code. While it offers precision, it often slows down experimentation.
Vibe coding accelerates development by automating much of the coding process. Developers can rapidly prototype ideas and iterate quickly. This speed is especially valuable for startups, hackathons, and exploratory projects.
Control and scalability
Traditional coding provides full control over architecture, performance, and security. It is well suited for large scale systems and mission critical applications.
Vibe coding may struggle in these areas. AI generated code can be difficult to optimize or audit, and it may not meet strict compliance or security requirements without significant refinement.
Role of the developer
In traditional development, developers write, test, and maintain the entire codebase themselves.
In vibe coding, developers act as guides and editors. They define goals, evaluate outputs, and adjust prompts. This role requires clarity of intent and the ability to assess whether results align with requirements.
Vibe coding versus AI assisted engineering
It is important to distinguish vibe coding from disciplined AI assisted engineering. In AI assisted engineering, AI tools support developers but do not replace careful review and understanding. Developers still maintain full responsibility for code quality and correctness.
Vibe coding, by contrast, often involves accepting AI outputs with less scrutiny, especially during early experimentation. The goal is speed and creativity rather than production readiness. While both approaches use AI, their expectations and practices differ significantly.
Vibe Coding vs Traditional Coding Infographic
Use cases where vibe coding excels
Vibe coding is particularly effective in certain scenarios where speed and accessibility matter more than long term maintainability.
Rapid prototyping
When testing new ideas or concepts, vibe coding allows teams to build working prototypes quickly. This enables faster feedback and better decision making.
Learning and exploration
Beginners can use vibe coding to learn how software works by experimenting and observing results. It provides immediate gratification and encourages curiosity.
Small personal projects
For side projects or weekend experiments, vibe coding reduces friction and allows creators to focus on creativity rather than technical hurdles.
Non technical users building tools
Professionals in fields such as finance, marketing, or operations can build custom tools without relying on developers, simply by describing their needs.
Limitations and risks of vibe coding
Despite its advantages, vibe coding has notable limitations that developers must consider.
AI generated code may contain inefficiencies, security vulnerabilities, or logical errors. Without careful review, these issues can go unnoticed.
Vibe coding may also produce code that is difficult to maintain or scale. Because the structure is determined by AI, it may not align with best practices or organizational standards.
Additionally, over reliance on vibe coding can reduce opportunities for developers to deepen their technical skills, potentially leading to knowledge gaps.
Impact on the future of software development
Vibe coding represents a broader trend toward higher level abstraction in software development. As tools become more capable, the role of developers is shifting from writing code to defining problems and evaluating solutions.
This does not mean traditional coding will disappear. Instead, hybrid models are likely to emerge, combining the speed and accessibility of vibe coding with the rigor and control of manual development.
Organizations may use vibe coding for early stage exploration and then transition to traditional methods for production systems. Developers who can effectively combine both approaches will be especially valuable.
Ethical and professional considerations
The rise of vibe coding raises important questions about responsibility and accountability. If AI generates code that causes errors or security breaches, developers must still take ownership of outcomes.
There is also a need for transparency. Teams should understand when and how AI generated code is used, especially in professional environments.
Maintaining standards of quality and ethics remains essential, regardless of how code is produced.
Best practices for implementing vibe coding
To use vibe coding effectively, developers should follow several best practices.
| Best Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Define goals and constraints clearly | Clearly define goals and constraints in prompts to reduce ambiguity and improve AI generated results |
| Test generated code | Test generated code thoroughly, even for small projects, to catch errors and unexpected behavior |
| Use as a starting point | Use vibe coding as a starting point rather than a final solution for complex systems |
| Learn traditional development | Continue learning traditional development principles to better evaluate and improve AI outputs |
| Combine with disciplined review | Combine vibe coding with careful review and testing when moving toward production |
Tools commonly used for vibe coding
Vibe coding typically involves AI powered development platforms that support conversational interaction. These tools translate natural language instructions into executable code and allow iterative refinement.
Such platforms often integrate with development environments, making it easy to test and modify results. The choice of tool depends on project needs, supported languages, and user experience.
Vibe coding and democratization of software creation
One of the most significant impacts of vibe coding is its role in democratizing software development. By removing many technical barriers, it empowers a broader range of people to create digital solutions.
This can lead to greater innovation, as diverse perspectives bring new ideas and applications. It also reduces dependency on specialized developers for simple tools, increasing efficiency across industries.
Long term implications for developers
As vibe coding becomes more common, developers will need to adapt. Skills such as problem framing, critical thinking, and system design will become even more important.
Understanding how to communicate effectively with AI systems will be a valuable skill. Developers who can balance creativity with technical rigor will thrive in this evolving landscape.
Conclusion
Vibe coding is an innovative software development approach that uses artificial intelligence to generate code from natural language prompts. It prioritizes speed, creativity, and accessibility, making it ideal for prototyping, learning, and small projects. While it cannot replace traditional coding for complex or critical systems, it represents a powerful addition to the developer toolkit and signals a shift toward more intuitive ways of building software.
Frequently asked questions
Is vibe coding suitable for production software?
Vibe coding is best suited for prototypes and small projects. Production software usually requires deeper review, testing, and control.
Do I need programming knowledge to use vibe coding?
Basic understanding helps, but vibe coding allows even non technical users to build functional applications.
How is vibe coding different from no code platforms?
Vibe coding uses conversational AI to generate custom code, offering more flexibility than fixed no code interfaces.
Can vibe coding replace traditional developers?
It is unlikely to replace them entirely. Instead, it changes how developers work and what skills matter most.
Is vibe coding secure?
Security depends on review and testing. AI generated code should always be evaluated for vulnerabilities before serious use.

Dony Garvasis is the founder of Search Ethics, a platform dedicated to transparency, authenticity, and ethical digital practices. With over 8 years of experience in SEO and digital marketing, I provide expert content on Tech, digital marketing, SEO, Artificial intelligence, gadgets, science, automobiles, lifestyle, tips, tutorials and much more. My mission is simple: Ethical Search, Genuine Results! I will make sure people everywhere get trustworthy and helpful information.